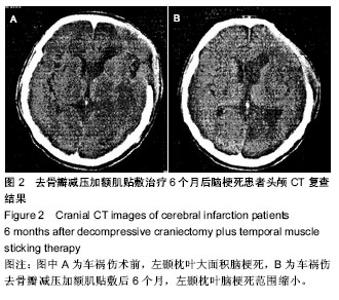
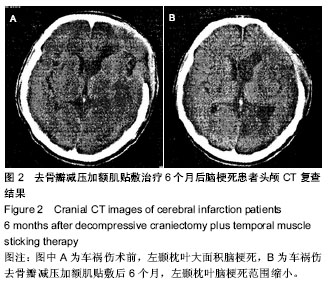
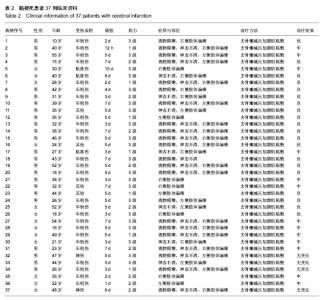
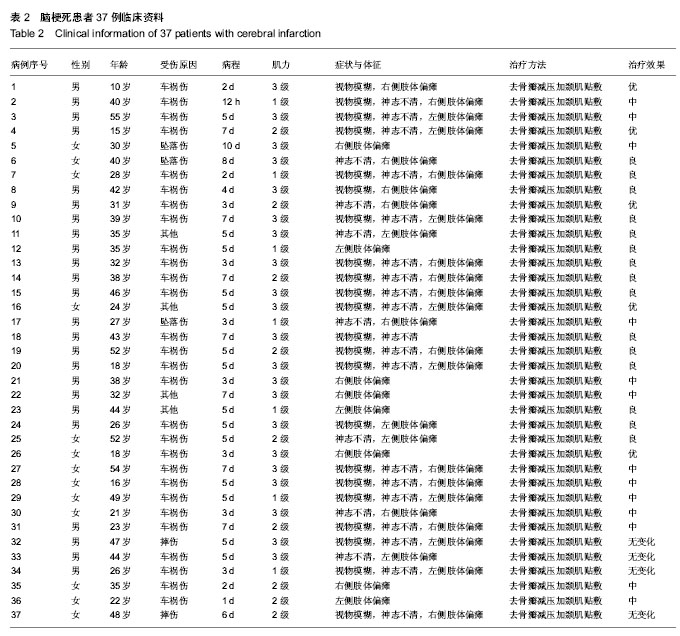
| [1] 高文杰,唐云华.MRI与CT在老年多发性脑梗死患者诊断中的临床结果对比[J].中国医药指南,2014,12(3):52-53.[2] 杜飞,郭艳霞.MRI与CT在老年多发性脑梗死病人诊断中的临床结果比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(3):487-489.[3] 车现涛,张宁.MRI和CT对多发性脑梗死的诊断价值探讨[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(19):77-78.[4] 朱丰裕.58例老年多发性脑梗死患者MRI与CT诊断的对比分析[J].现代诊断与治疗, 2012,23(10):1622-1623.[5] 杨扬,于洋洋.MRI与CT在老年多发性脑梗死病人诊断中的临床结果对比[J].中外健康文摘,2013,10(19):226-226,227.[6] 李素花.65例大面积脑梗死患者早期CT诊断的临床价值分析[J].中外健康文摘,2013,10(26):169-169.[7] 姜庆,陈吉妍.外伤性脑梗死的多层螺旋CT表现和诊断[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(19):604-605.[8] 徐建中,赵金华.MRI和CT应用于多发性脑梗死的诊断价值探讨 [J].医学信息(下旬刊), 2013,26(10):304-305.[9] 周沛华.MRI与CT在老年多发性脑梗死病人诊断中的临床结果对比[J].健康之路, 2013,12(4):309.[10] 李君权,徐小东. MRI与CT在老年多发性脑梗死诊断中的临床价值分析[J].医学影像学杂志, 2013,23(12):2034-2036. [11] 李日健,许均黎.老年多发性脑梗死患者MRI与CT结果的对比分析[J].广东医学院学报, 2000,18(2):207-208.[12] 张晖.依达拉奉注射液治疗急性脑梗死分析[J].中国伤残医学, 2014,22(1):119.[13] 贾书稳,魏文志,马俊清.依达拉奉联合长春西汀治疗急性脑梗死的疗效观察[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2010,18(9):1275- 1276.[14] 姚丽娟,张振东,张秋实,等.联合用药对急性脑梗死临床治疗效果的观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(19):584-585.[15] 曹秀梅,应风博.依达拉奉、长春西汀、疏血通联合治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效及对血液流变学的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2012, 32(20):4515-4516.[16] 鄢金枝,刘静.高压氧联合药物治疗急性脑梗死患者的临床疗效观察[J].世界最新医学信息文摘(电子版),2013,13(14):205[17] 向云,尉洋.综合康复治疗联合叶酸甲钴胺对脑梗死患者血同型半胱氨酸水平的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2013, 11(6):653-655[18] 杨勇,于临源.分水岭脑梗死行介入治疗的临床疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(32):144-145. [19] 凌维汉,俞万香,丘为,等.大面积脑梗死患者介入治疗的临床效果观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(17):135-136.[20] 何劲松.微创介入治疗对急性脑梗死患者血清NGF、NTF、VEGF细胞因子的影响[J].中国医药导报,2013,10 (1):51-52. [21] 何国祥.脑梗死动脉介入溶栓与非介入治疗对比分析[J].中外医疗,2013,32(2):65-66. [22] 裘丽红,韩新生.选择性动脉介入溶栓治疗急性脑梗死临床疗效观察[J].临床荟萃, 2005,20(19):1107-1108.[23] 李志丹,孙华山,刘世丽,等.228例急性缺血性脑血管病动脉介入溶栓治疗的效果[J].神经疾病与精神卫生,2011,11(5):498-500.[24] Kim DJ,Kim DI,Byun JS. Intraarterial thrombolytic therapy for hyperacute ischemic stroke caused by tandem occlusion. Cerebrovasc Dis.2008;26(2):184-189.[25] Linfante I,Llinas RH,Selim M,et al.Clinical and vascular outcome in internal carotid artery versus middle cerebral artery occlusions after intravenous tissue plasminogen activator.Stroke.2002;33:2066-2071. [26] Srinivasan A,Goyal M,Stys P,et al.Microcatheter navigation and thrombolysis in acute symptomatic cervical internal carotid occlusion.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2006;27:774-779. [27] Wang H,Wang D,Fraser K,et al.Emergent combined intracranial thrombolysis and carotid stenting in the hyperacute management of stroke patients with severe cervical carotid stenosis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2007; 28:1162-1166. [28] Schomer DF,Marks MP,Steinberg GK,et al.The anatomy of the posterior communicating artery as a risk factor for ischemic cerebral infarction. N Engl J Med.1994;330: 1565-1570. [29] 张秀卿,张涛,金晓,等.去骨瓣减压联合硬膜扩大缝合术治疗大面积脑梗死[J].中国实用医刊,2012,39(2):91-92.[30] 刘庆国,宋志斌,高建伟,等.去骨瓣减压手术治疗恶性大脑中动脉脑梗死的手术时机探讨[J].长治医学院学报,2011,25(1): 26-28.[31] 田洪奎.大面积脑梗死的外科治疗26例临床分析[J].中国医学创新,2009,6(1):33-35. [32] 陆伟水,甘渭河,汤树洪,等.手术治疗大面积脑梗死8例临床分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2009,26(2):300-301. [33] 李杨,刘东华,石伏军.外伤性大面积脑梗死21例手术治疗体会[J].宁夏医学杂志,2008,30(10):917-918.[34] 石新刚.外科手术治疗大面积脑梗死10例分析[J].中国社区医师(医学专业), 2011,13(14):227. [35] 曲东锋.颅骨切除减压治疗恶性大脑中动脉梗死试验(DECI- MAL) [J].围外医学:脑血管疾病分册,1997,7(4):281.[36] 于朝春,段国升,余新光,等.小脑幕裂孔疝致颅内血管闭塞[J].中华神经外科杂志,1995,13(4):241.[37] 陶胜忠,张鹏远,苗旺,等.去骨瓣减压术治疗大面积脑梗死16例临床分析[J].中国神经精神疾病杂,2005,31(3):234-235.[38] Michael Diringer.恶化型大脑半球大面积脑梗死的处理[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2003,29(1):1-6.[39] 刘志坚,蒋健,王嵘,等.标准大骨瓣减压并颞肌贴敷术治疗大面积脑梗死[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2005,10(2):96-97.[40] 张庆林,壬成伟.神经外科手术规范及典型病例点评[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社,2004:380-381.[41] 周良辅.现代神经外科学[M].上海:复旦大学出版社,2001: 781-787.[42] Mori K,Nakao Y,Yamamoto T,et al.Early external decompressive craniectomy with duroplasty improves functional recovery in patients with massive hemispheric embolic infarction: timing and indication of decompressive surgery for malignant cerebral infarction.Surg Neurol.2004; 62(5):420-429.[43] Mori K,Aoki A,Yamamoto T,et al.Aggressive decompressive surgery in patients with massive hemispheric embolic cerebral infarction associated with severe brain swelling.Acta Neurochir (Wien).2001;143(5):483-491.[44] Engelhorn T,Dörfler A,Egelhof T,et al.Follow-up monitoring with magnetic resonance tomography after decompressive trephining in experimental "malignant" hemispheric infarct. Zentralbl Neurochir.1998;59(3):157-165.[45] Arac A,Blanchard V,Lee M,et al.Assessment of outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction in patients older than 60 years of age.Neurosurg Focus.2009;26(6):E3. |